How to Quit a Method in Java Using Q to Quit or Looping the Condition Again
In computer programming, loops are used to repeat a block of code.
For example, let's say we want to show a message 100 times. Then instead of writing the print statement 100 times, we can use a loop.
That was just a simple example; we can achieve much more efficiency and sophistication in our programs by making effective use of loops.
There are 3 types of loops in C++.
-
forloop -
whileloop -
do...whileloop
In the previous tutorial, we learned about the C++ for loop. Here, we are going to learn about while and do...while loops.
C++ while Loop
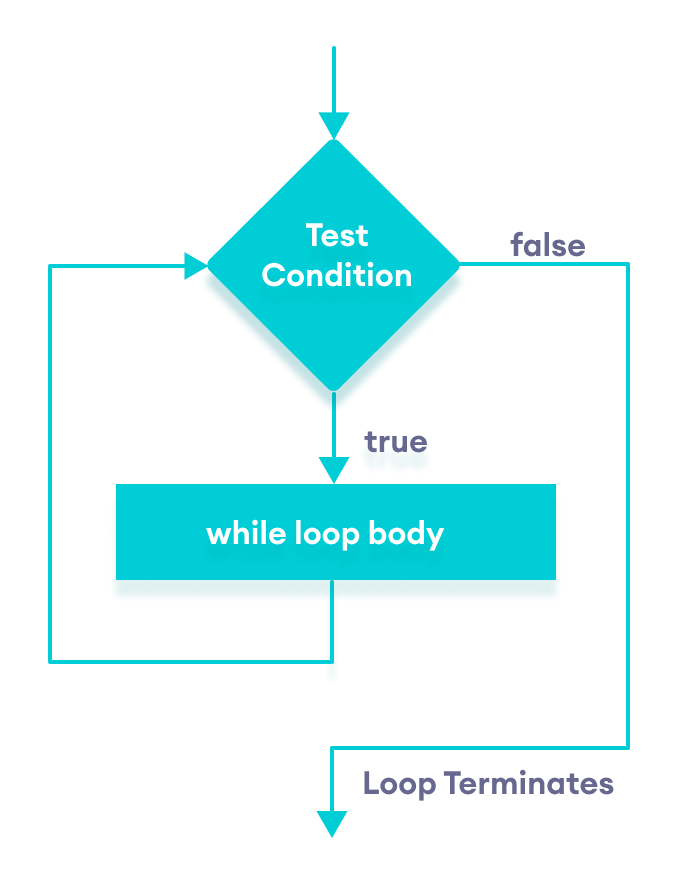
The syntax of the while loop is:
while (condition) { // body of the loop } Here,
- A
whileloop evaluates thecondition - If the
conditionevaluates totrue, the code inside thewhileloop is executed. - The
conditionis evaluated again. - This process continues until the
conditionisfalse. - When the
conditionevaluates tofalse, the loop terminates.
To learn more about the conditions, visit C++ Relational and Logical Operators.
Flowchart of while Loop
Example 1: Display Numbers from 1 to 5
// C++ Program to print numbers from 1 to 5 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i = 1; // while loop from 1 to 5 while (i <= 5) { cout << i << " "; ++i; } return 0; } Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here is how the program works.
| Iteration | Variable | i <= 5 | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | i = 1 | true | 1 is printed and i is increased to 2. |
| 2nd | i = 2 | true | 2 is printed and i is increased to 3. |
| 3rd | i = 3 | true | 3 is printed and i is increased to 4 |
| 4th | i = 4 | true | 4 is printed and i is increased to 5. |
| 5th | i = 5 | true | 5 is printed and i is increased to 6. |
| 6th | i = 6 | false | The loop is terminated |
Example 2: Sum of Positive Numbers Only
// program to find the sum of positive numbers // if the user enters a negative number, the loop ends // the negative number entered is not added to the sum #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int number; int sum = 0; // take input from the user cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> number; while (number >= 0) { // add all positive numbers sum += number; // take input again if the number is positive cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> number; } // display the sum cout << "\nThe sum is " << sum << endl; return 0; } Output
Enter a number: 6 Enter a number: 12 Enter a number: 7 Enter a number: 0 Enter a number: -2 The sum is 25
In this program, the user is prompted to enter a number, which is stored in the variable number.
In order to store the sum of the numbers, we declare a variable sum and initialize it to the value of 0.
The while loop continues until the user enters a negative number. During each iteration, the number entered by the user is added to the sum variable.
When the user enters a negative number, the loop terminates. Finally, the total sum is displayed.
C++ do...while Loop
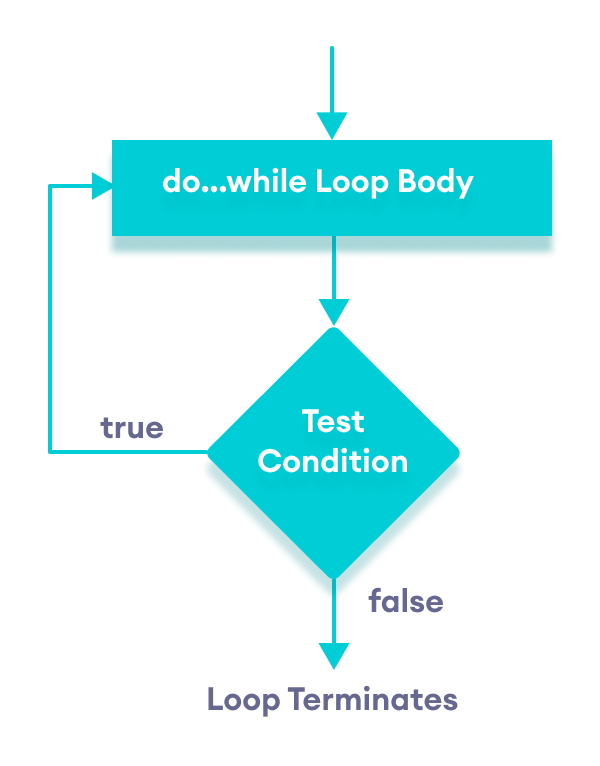
The do...while loop is a variant of the while loop with one important difference: the body of do...while loop is executed once before the condition is checked.
Its syntax is:
do { // body of loop; } while (condition); Here,
- The body of the loop is executed at first. Then the
conditionis evaluated. - If the
conditionevaluates totrue, the body of the loop inside thedostatement is executed again. - The
conditionis evaluated once again. - If the
conditionevaluates totrue, the body of the loop inside thedostatement is executed again. - This process continues until the
conditionevaluates tofalse. Then the loop stops.
Flowchart of do...while Loop
Example 3: Display Numbers from 1 to 5
// C++ Program to print numbers from 1 to 5 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i = 1; // do...while loop from 1 to 5 do { cout << i << " "; ++i; } while (i <= 5); return 0; } Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here is how the program works.
| Iteration | Variable | i <= 5 | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
i = 1 | not checked | 1 is printed and i is increased to 2 | |
| 1st | i = 2 | true | 2 is printed and i is increased to 3 |
| 2nd | i = 3 | true | 3 is printed and i is increased to 4 |
| 3rd | i = 4 | true | 4 is printed and i is increased to 5 |
| 4th | i = 5 | true | 5 is printed and i is increased to 6 |
| 5th | i = 6 | false | The loop is terminated |
Example 4: Sum of Positive Numbers Only
// program to find the sum of positive numbers // If the user enters a negative number, the loop ends // the negative number entered is not added to the sum #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int number = 0; int sum = 0; do { sum += number; // take input from the user cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> number; } while (number >= 0); // display the sum cout << "\nThe sum is " << sum << endl; return 0; } Output 1
Enter a number: 6 Enter a number: 12 Enter a number: 7 Enter a number: 0 Enter a number: -2 The sum is 25
Here, the do...while loop continues until the user enters a negative number. When the number is negative, the loop terminates; the negative number is not added to the sum variable.
Output 2
Enter a number: -6 The sum is 0.
The body of the do...while loop runs only once if the user enters a negative number.
Infinite while loop
If the condition of a loop is always true, the loop runs for infinite times (until the memory is full). For example,
// infinite while loop while(true) { // body of the loop } Here is an example of an infinite do...while loop.
// infinite do...while loop int count = 1; do { // body of loop } while(count == 1); In the above programs, the condition is always true. Hence, the loop body will run for infinite times.
for vs while loops
A for loop is usually used when the number of iterations is known. For example,
// This loop is iterated 5 times for (int i = 1; i <=5; ++i) { // body of the loop } Here, we know that the for-loop will be executed 5 times.
However, while and do...while loops are usually used when the number of iterations is unknown. For example,
while (condition) { // body of the loop } Check out these examples to learn more:
- C++ Program to Display Fibonacci Series
- C++ Program to Find GCD
- C++ Program to Find LCM
staufferinece1988.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.programiz.com/cpp-programming/do-while-loop
0 Response to "How to Quit a Method in Java Using Q to Quit or Looping the Condition Again"
Post a Comment